Key Facts:
- Meningococcal B is one of the strains of meningococcal
- Meningococcal is a serious infectious disease that can cause severe scarring, loss of limbs, brain damage and death.
- Those most at risk of Meningococcal B are infants, small children, adolescents, young adults and Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people aged 2 months to 19 years
- Vaccination is your best protection against the Meningococcal B strain and is available in Australia.
Meingococcal B Vaccination
The Australian Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (ATAGI) recommends vaccines in Australia.
Vaccines are available in Australia to reduce the risk of Meningococcal B.
Under the Federal government's National Immunisation Program (NIP) the Meningococcal B vaccine is free for:
- Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander children 12 months and under
- people with asplenia and hyposplenia
State government programs might also provide funding for vaccination. South Australia and Queensland extend free Meningococcal B vaccination to specific groups.
We recommend to speak with your GP about Meningococcal B vaccination for children under 5 years of age.
 Vaccination is the best protection against Meningococcal B
Vaccination is the best protection against Meningococcal B
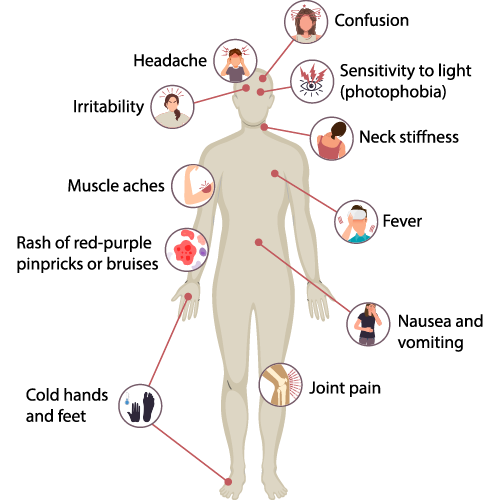
Meningococcal B Symptoms
Symptoms may appear 1–10 days after being infected.
People with meningococcal disease can become extremely unwell quickly.
Symptoms can include:
- Confusion
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Neck Stiffness
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Muscle Aches
- Rash of red-purple pin pricks or bruises
- Cold hands and feet
- Joint Pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
How it spreads
Infected secretions from the back of the nose & throat.

Coughing

Sneezing

Regular, close, prolonged household or intimate contact
